Expressive Score-Based Priors for Distribution Matching with Geometry-Preserving Regularization
Abstract
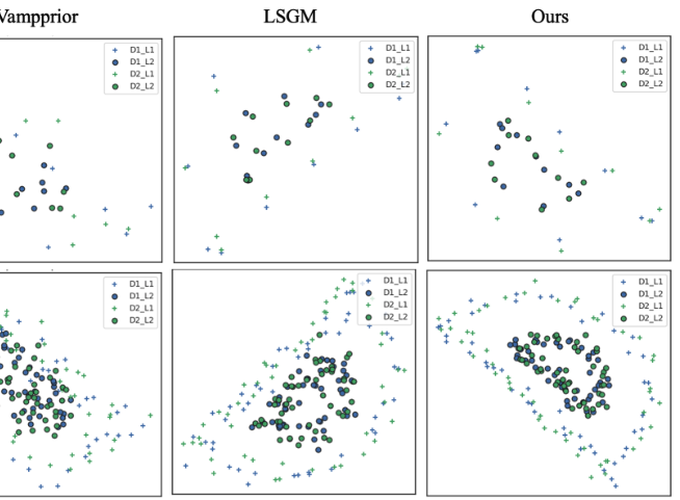
Distribution matching (DM) is a versatile domain-invariant representation learning technique that has been applied to tasks such as fair classification, domain adaptation, and domain translation. Non-parametric DM methods struggle with scalability and adversarial DM approaches suffer from instability and mode collapse. While likelihood-based methods are a promising alternative, they often impose unnecessary biases through fixed priors or require explicit density models (e.g., flows) that can be challenging to train. We address this limitation by introducing a novel approach to training likelihood-based DM using expressive score-based prior distributions. Our key insight is that gradient-based DM training only requires the prior’s score function—not its density—allowing us to train the prior via denoising score matching. This approach eliminates biases from fixed priors (e.g., in VAEs), enabling more effective use of geometry-preserving regularization, while avoiding the challenge of learning an explicit prior density model (e.g., a flow-based prior). Our method also demonstrates better stability and computational efficiency compared to other diffusion-based priors (e.g., LSGM). Furthermore, experiments demonstrate superior performance across multiple tasks, establishing our score-based method as a stable and effective approach to distribution matching. Source code available at https://github.com/inouye-lab/SAUB.